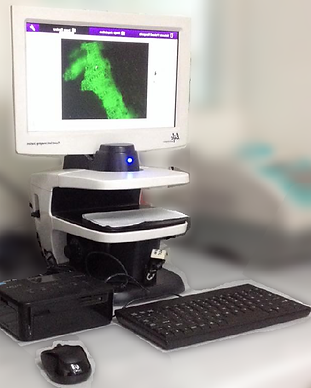
Imaging System
Cellular imaging; detection and verification of fluorescently-labeled samples that uses a fixed 20x plan fluorite objective. Fluorescence is captured using DAPI, FITC, and Texas Red filters, the three most commonly used channels. It has 460X (optical) to 1840X (with digital zoom) and comes in different format: cell culture dish, cell culture flask (T75), cell culture plate (multi-well), coverslip(s), petri dish, and slide(s).

Thermal cycler
PCR machine: Laboratory equipment used for Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). This is usually used for amplification of gene of interest acquired from a sample.

Spectrophotometer
Laboratory apparatus used for measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a material as a function of wavelength. This is usually used to quantify solutions of nucleic acids and proteins.

Micropipettors
Laboratory instrument used to transport a measured volume of liquid, often as a media dispenser.

Microplate reader
Laboratory apparatus used to detect or quantify realtive absorbance, fluorescence, luminescence, light scattering and nephelometry; ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) reader

Ultralow freezer
-80°C lab freezers; usually used for long term storage of biological samples.

Gel Imaging System
Laboratory appratus/system used for detecting, imaging, and quantitating multiplex fluorescence, chemiluminescence, stain-free and colorimetric blots and gels.

Microwave oven
Appliance that heats and cooks food by exposing it to electromagnetic radiation in the microwave frequency range; (in the lab) used for heating agarose gel.

Centrifuge
Laboratory equipment driven by motor that puts an object in rotation around a fixed axis, applying a potentially strong force perpendicular to the axis of spin.

Freeze Dryer
Laboratory apparatus used for dehydration of samples for the purpose of preservation of a perishable material and/or for conveniency of transport.

Top Loading Balance
A class of balance designed to measure small mass in the sub-milligram range.

Centrifuge
Scientific instrument that measures the hydrogen-ion activity in water-based solutions, indicating its acidity or alkalinity expressed as pH

Ice crusher
Equipment used to crush ice to be used for experiments as a means of temporary storage.

Electrophoresis Apparatus
Laboratory equipment that applies an electric charge to molecules causing them to migrate towards their oppositely charged electrode. This is usually utilized for DNA and protein applications, and is classified into gel and capillary techniques.

Fragment Analyzer
A parallel capillary electrophoresis instrument designed to reduce bottle necks in automation process (gel loading, sampe injection, etc) and to analyze nucleic acid fragment using PROSize® software.

Water Bath
Laboratory equipment made from a container filled with heated water to incubate samples in water at a constant temperature over a long period of time.

Autoclave
Laboratory apparatus used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to high-pressure saturated steam at 121 °C for 15–20 minutes depending on the size of the load and the contents.

Laminar Flow Hood
Laboratory equipment that provides an aseptic work area while allowing the containment of infectious splashes or aerosols generated by many microbiological procedures.

Platform Shaker
Laboratory equipment used for a gentle, rocking motion required for certain applications like low foaming agitation, DNA extraction, washing blots and various staining procedures.

Glass Bead Sterilizer
Commonly used to sterilize forceps, scissors, tweezers, scalpels, needles, inoculation loops and etc.

Vortex Mixer
A simple lab apparatus commonly used in laboratories to mix small vials of liquid.
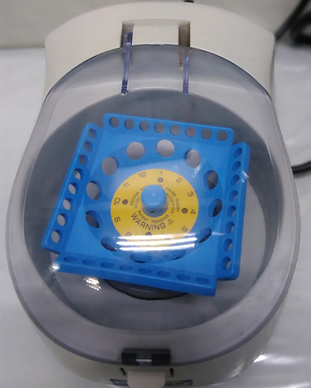
Mini Microcentrifuge
A simple lab apparatus commonly used in laboratories to mix small vials of liquid. Used to spin down liquids for a short period of time instead of using a bigger.

Steroscopic Microscope
Dissecting microscope; an optical microscope variant designed for low magnification observation of a sample, typically using light reflected from the surface of an object rather than transmitted through it.

Compound Microscope
A microscope with more than one lens and has its own light source. In this type of microscope, there are ocular lenses in the binocular eyepieces and objective lenses in a rotating nosepiece closer to the specimen. Also, the sample’s contrast comes from its absorption of the light.

_svg.png)